This post covers new feature ZONESintroduced in Solaris 10, zone is virtualized solaris operating system within Solaris. You can install multiple Solaris Operating System (Multiple Machine) with in Single Big Machine. This will help in consolidating multiple small Solaris machine into one big machine with multiple Solaris operating system each running different application.
Zones: is virtualized operating system created with in single instance of Solaris operating system.
Container : Zone which includes resource management feature is called as container.
Key Points for Solaris 10 Zones
1. Zones can be created on any machine running Solaris 10
2. Maximum number of zones (virtualised solaris o.s.) is 8192
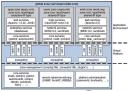
3. Master zone or base operating system is called as Global Zoneand any zone (virtualised Solaris o.s.) created is called as Non-Global zone.
In figure serviceprovider.com is global zone where as apps.com , users.net and work.org are Non-Global zone.
4. Non global zones can only be created, managed, configured or uninstalled from Global zone.
5. Each zone (global & non global) is assigned a name and global zone always has zone name as global. Each zone is also given number ID and for global zone ID/zone number is always 0.
6. Each zone has path to its root directory which is relative to global zone’s root directory.
7. Root File system on non-global zone are of two type : Sparse and Whole root
Whole root file system provide more flexibility where as Sparse root zone model provide maximum configuration.
8. Dynamic resource reallocation permits unused resource to be shifted to other containers (aka zones)
9. Process within same zone can communicate each other but if process in one zone need to communicate with process in other zone, they can do it only by using network APIs.
10. IP networking can be configured with each zone having its own exclusive IP address or can share IP layer configuration and state with global zone (aka shared-IP zone).
11. IP configuration of an exclusive-IP can only be viewed from global zone using zlogin like
zlogin my-zone ifconfig -a
12. You use “zonecfg” command to configure a non-global zone
13. You use “zlogin” to login to a zone from global zone
14. “zoneadm” is used to administer zone including installation, stopping, starting.
15. Parameters changed using zonecfg don’t affect running zone, you have to restart zone using “zoneadm -z zone_name reboot”
Related
Zones and Container FAQ
Solaris 10 is free and you can download(X86 or Sparc) or order from here (Opensolaris and Solaris 10 are different, go for Solaris 10 5/08 which means Solaris 10 May 2008 release)
