SSL configuration in OVD – Oracle Virtual Directory
This post covers key points and documentation to configure SSL in Oracle Virtual Directory (OVD) 11g. For SSL configuration in OID 11g click here
1. SSL Authentication Mode – OVD and any other SSL listener can be configured in one of three Authentication Mode
a. SSL No-Auth Mode : Neither client nor server are required to authenticate by showing their certificate. This mode is also called as anonymous or no authentication mode.
b. Server Authentication Mode : In this mode Server Authenticate itself to client by presenting SSL certificates but client does not Authenticate itself using certificate. This mode is also called as one-way SSL or Server authentication.
c. Mutual Authentication : In this mode both client and server authenticates each other using SSL certificates. This mode is also called as two-way SSL or Client authentication.
Note: OVD SSL Listener by default is configured in Server Authentication Mode.
2. OVD by default listens on four ports (More on OVD listeners here)
a) LDAP Listener – Non SSL LDAP default port 6501
b) LDAPS Listener – SSL LDAP default port 7501
c) Admin Listener – SSL Admin port 8899
d) DSML Gateway – Non SSL HTTP port 8080
Note: Client’s usually connect to OVD using LDAP or LDAPS Listener
3. LDAPS and Admin Gateway Listener by default comes with SSL with self signed certificate. You can change from self signed certificates to certificates issues trusted CA like Verisign/Thawte or you can use your own CA.
4. SSL certificates (issued to OVD listeners) and Certifying Authority’s Certificates (Certificates of Authority that issues these certificate ) are stored in Keystore.
5. Keystore – In Oracle Fusion Middleware there are two type of keystores.
a) JKS Keystore and Truststore (aka Java Key Store)
b) Oracle Wallets
Note : OVD uses Java Key Store to store certificates. System Components of Fusion Middleware like OID & OHS uses Oracle Wallets to store SSL certificates.
6. You can configure/manage SSL in OVD (LDAPS listener) using
a) WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST)
or
b) Fusion Middleware Enterprise Manager Control (/em)
Note: To manage SSL certificates using EM or WLST, OVD must be configured with Weblogic Server with EM application deployed .
7. Java Keystore lifecycle includes
a) Creating keystore
b) viewing/updating keystore
c) exporting/importing keystore
d) deleting keystore
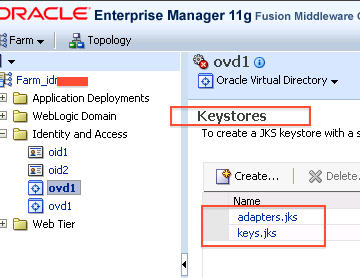
8. To create/manage keystore in OVD –
a) Login to EM
b) Navigate to ovd -> Security -> Keystores

9. OVD by default creates following Keystore
a) keys.jks (Trust Store and SSL Keys for OVD LDAPS Listeners)
b) Optional – If LDAP Adapter using TLS/SSL is defined then adapters.jks (containing SSL certificate and trust store for OVD to LDAP connection on SSL )
10. Location of Key Store for OVD LDAPS Listener is defined in OVD EM : Administration -> Listeners -> LDAP SSL End Point (Edit) -> Change SSL Settings
11. Location of Key Store for OVD LDAP Adapter is defined in OVD EM : Administration -> Server Properties (Under TLS Configuration Section)
12. Java Keystore (JKS) for OVD is stored on File System under $ORACLE_INSTANCE/config/OVD/[ovd1]/keystores
13. If you don’t want to use self signed certificate and wish to use certificates signed by trusted certifying certificate (like verisign or thawte) or signed by your companies PKI then
a. Create Java keystore using /em or wlst
b. Generate CSR (Certificate Signing Request)
c. Send CSR to Certifying Authority (CA) for signing the certificates
d. Once you get signed certificate from CA (Certifying Authority) then import signed certificate in to keystore
e. If certificates are signed by companies PKI then ask OVD clients (including ODSM) to include CA’s certificates (as trusted certificate)
Note: Certificates can be DER-encoded or Base-64 encoded format. You cannot use FMW control to import DER-encoded certificate.
References/Further Reading
- Enabling SSL on Oracle Virtual Directory Listeners in FMW Admin Guide
- Managing Key Store, Wallets and Certificates
- Master Note for SSL Configuration in Fusion Middleware 11g [ID 1218695.1]